previous unit : stakeholders
Next unit : Multinational Companies (MNCs)
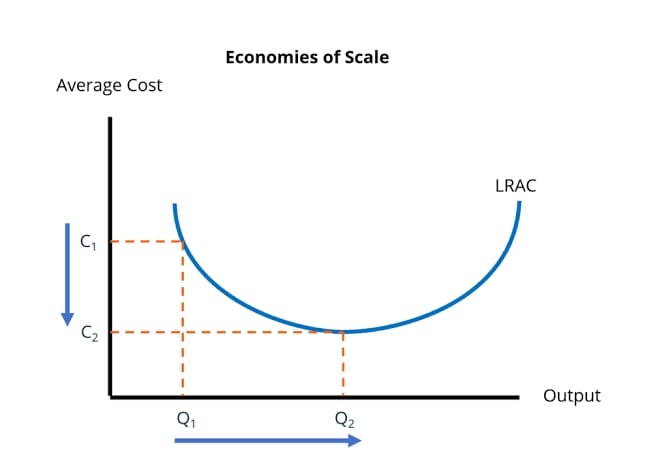
Economies of Scale
What is Economies of Scale
- Occurs when the average cost of production decreases as the output increases
- It happens due to improvement in efficiency
What is Diseconomies of Scale
- Occurs when the average cost of production increases as the output increases
- It happens due to a decrease in efficiency
[ Internal ]
Technical
- Large business can buy costly and large-sized machinery and technology which is faster and / or more efficient and hence can produce higher output
- This decreases the average cost of production as the cost of machinery / technology is distributed over a large size of output
Financial
- Large firms require higher levels of finance hence they can negotiate a cheaper interest from the lender
- Large firms have lower risk of failure and hence lenders may be more willing to give a lower rate of interest
Managerial
- Large firms have specialization of the managerial and labour level. Manager may specialize in marketing, finance and labour in their respective skill set.
- Specialisation increase productivity / efficiency which decrease average cost of production
Purchasing
- Large firms place larger orders with the suppliers and can negotiate better terms like higher discount, faster delivery etc.
Marketing
- Large firms may be able to negotiate lower sales commission, lower credit card period, lesser profit margin from their customers.
- They are able to spread the communication cost across the output.
[ External ]
Infrastructure
- Improved infrastructure of the economies may lead to lower transportation costs, increased access to utilities and better connectivity
Education
- Improved education level and training in the locality may increase the productivity of labour
Clustering
- As businesses cluster together in the area, all the business benefit from access to specialized labour and other services
Technology
- Growth in the economy may lead to improved technology for supplier which would reduce the cost of raw materials
Diseconomies of Scale
[Internal]
Communication and Coordination
- As firms become larger, communication may not reach to all intended parties in the right time
- Coordination among employees / department may be difficult as different managers have different styles and preferences
Lack of Motivation
- Large firms may have increased level of hierarchy.
- This may make it hard for employees from interacting with their managers and the owners on a regular basis.
- This may demotivate them, which can reduce employee efficiency and the efficiency in the operation of the business.
Complancency
- Large firms may be complacent with their ways of working and may not identify threats or opportunities.
- Smaller rival firms may be able to do things better than the larger ones.
[External]
Higher Inflation
- There may be a high rate of inflation causing the resources to be costlier which may increase rental costs and salaries
Higher Taxes
- Higher trade protection in the form of import tax may result in higher cost of resources. Can be any tax.
Reasons for a business to grow
- Success is usually associated with growth and it’s highly satisfying for the owners / investors to grow their business
- A large business:
- Is financially more sustainable and has lesser risk of failure
- Benefits from economies of scale and is able to influence suppliers, customers, lenders, etc.
- Attract potential investors and human
- Is financially more sustainable and has lesser risk of failure
The two types of Growth
Internal Growth
- Refers to growth when the business uses it’s internal resources to grow
- Use retained profits and owners’ personal funds as a source of finance
- BM term - Organic Growth
External Growth
- Refers to growth when the business grows by taking large financial capital or resources from parties outside the business like other business or large investors
- BM term - Inorganic Growth
Differences between Internal and External Growth
| Speed of growth | Relatively Low | Relatively High |
| Loss of Ownership | Less | More |
| Change in work culture | Less | More |
| Access to talent and ideas | Less | More |
| Causes of Failure | Lack of scale | Mismatch of culture |
| Increased Competion | Failure to exploit |